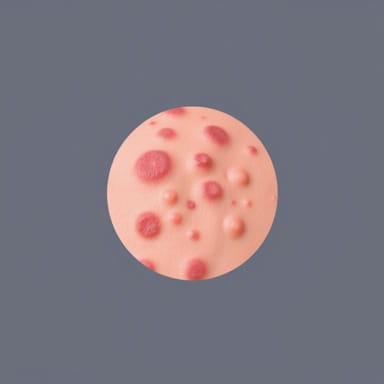
Pustular psoriasis is a rare and severe form of psoriasis characterized by widespread pustules on inflamed skin, often accompanied by redness, scaling, and pain. Unlike the more common plaque psoriasis, pustular psoriasis can appear suddenly and may lead to systemic symptoms such as fever, chills, and fatigue. Because of its intensity and potential complications, effective treatment of pustular psoriasis requires prompt medical attention, a combination of topical, systemic, and lifestyle approaches, and careful monitoring to prevent flares and manage triggers.
Understanding Pustular Psoriasis
Pustular psoriasis can manifest in several forms, including generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP), palmoplantar pustulosis (affecting the hands and feet), and localized variants. The condition involves an abnormal immune response that triggers rapid skin cell turnover, leading to the formation of sterile pustules filled with white blood cells. This autoimmune component distinguishes pustular psoriasis from infections and other skin disorders, highlighting the importance of accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment.
Symptoms and Signs
The symptoms of pustular psoriasis vary depending on the type and severity, but common signs include
- Clusters of small, pus-filled blisters on red, inflamed skin
- Intense itching or burning sensation
- Scaling and peeling of affected areas
- Fever, malaise, and body aches in generalized cases
- Thickened skin on palms and soles in palmoplantar pustulosis
Immediate Management
For acute episodes, particularly generalized pustular psoriasis, rapid medical intervention is essential to prevent complications such as secondary infection, dehydration, or systemic inflammation. Hospitalization may be required in severe cases to provide intensive care, fluid replacement, and close monitoring of vital signs.
Identification of Triggers
Identifying and managing triggers is a cornerstone of treatment. Common triggers include
- Withdrawal of systemic corticosteroids
- Stress and hormonal changes
- Infections, particularly streptococcal infections
- Medications such as lithium, antimalarials, or beta-blockers
- Environmental factors, including cold weather or skin irritation
Topical Treatments
Topical therapy is often used in mild or localized pustular psoriasis to reduce inflammation, soothe irritation, and prevent progression. Key topical treatments include
Topical Corticosteroids
Potent corticosteroid creams or ointments can help reduce redness, swelling, and pustule formation. They are typically applied once or twice daily under medical supervision, with careful attention to prevent skin thinning or systemic absorption.
Moisturizers and Emollients
Regular use of moisturizers helps maintain skin barrier integrity, reduce scaling, and minimize discomfort. Emollients containing urea or ceramides may be particularly beneficial for thickened or peeling skin.
Coal Tar Preparations
Coal tar products may help slow skin cell turnover and reduce inflammation. While less commonly used for pustular psoriasis compared to plaque psoriasis, they can be adjunctive in certain localized cases.
Systemic Therapies
For moderate to severe pustular psoriasis, systemic medications are often required to control the disease and prevent flares. These therapies target the immune system and inflammatory pathways responsible for pustule formation.
Oral Retinoids
Acitretin, an oral retinoid, is commonly used for pustular psoriasis due to its ability to normalize skin cell growth and reduce pustule formation. Patients require monitoring for liver function, lipid levels, and potential teratogenic effects.
Immunosuppressive Agents
Medications such as cyclosporine or methotrexate can suppress the overactive immune response and rapidly control inflammation. Close monitoring of kidney function, liver function, and blood counts is essential to minimize side effects.
Biologic Therapies
Biologics, including TNF-alpha inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors, and IL-23 inhibitors, have revolutionized treatment for severe pustular psoriasis. These targeted therapies block specific immune pathways involved in pustule formation, offering rapid and sustained improvement in skin lesions. Biologics are often considered when patients do not respond to traditional systemic therapies or experience frequent relapses.
Adjunctive and Supportive Measures
Alongside medical treatments, supportive care is important for managing symptoms, preventing complications, and enhancing quality of life.
Managing Pain and Itching
- Topical or oral analgesics for pain relief
- Cool compresses or oatmeal baths to soothe itching and irritation
- Avoiding scratching to prevent secondary infections
Nutritional Support
Maintaining balanced nutrition supports skin healing and overall immune function. Patients should focus on a diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids while avoiding known dietary triggers if identified.
Infection Prevention
Because pustules are sterile but vulnerable to secondary infection, proper hygiene and wound care are essential. Topical antiseptics may be used cautiously, and any signs of bacterial infection should prompt immediate medical evaluation and potential antibiotic therapy.
Long-Term Management and Prevention
Preventing flares and maintaining remission is critical in pustular psoriasis. Long-term strategies include
- Regular follow-up with a dermatologist to adjust treatment plans
- Identifying and avoiding personal triggers such as medications or stress
- Maintaining consistent use of prescribed topical or systemic medications
- Stress management techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or counseling
- Monitoring for comorbidities, including metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk factors
Patient Education
Empowering patients with knowledge about their condition, treatment options, and self-care strategies is vital. Understanding early signs of flares, proper application of topical medications, and adherence to systemic therapies can significantly improve outcomes and reduce hospitalizations.
The treatment of pustular psoriasis requires a comprehensive, multi-faceted approach that addresses both the acute presentation and long-term disease management. Topical therapies, systemic medications, and biologics play central roles, while supportive care, trigger management, and lifestyle interventions help prevent recurrence and maintain skin health. Early diagnosis, timely intervention, and personalized treatment plans are essential to reduce discomfort, prevent complications, and improve quality of life for individuals affected by this challenging dermatological condition. With careful management and ongoing monitoring, many patients can achieve significant improvement and sustained control over their pustular psoriasis symptoms.